There’s a Pharmacist Behind Every Dose. Behind Every Pharmacist. There's Baxter.

Baxter’s Pharmacy Portfolio Has You Covered
We help you support patient care by minimizing risk due to compounding errors,1,2 maximizing efficiency and delivering value with the simplicity of a dedicated partner for ready-to-use intravenous (IV) medications.

Extensive Portfolio of Baxter’s Pharmacy Products
Baxter is constantly investing and innovating to help support patient care. Our products are available in a variety of presentations including ready-to-use IV formulations, vials, pre-filled syringes, tablets, bottles and transdermal systems.
Vials and Other Injectable Medications

Therapy Areas We Cover
Baxter offers a wide range of therapy areas to ensure broad coverage for your healthcare facility.
Learn about our Anesthesia medications
Learn about our Anti-Infective medications
Learn about our Critical Care medications
Learn about our Cardiac medications

The Baxter Commitment
With an innovative portfolio replenished by a pipeline of 20 new product launches slated by 2026 and a broad manufacturing and distribution network, Baxter is committed to saving and sustaining lives.
Featured Product Launches
Convenient ways to place your order
How might your facility benefit from adding Baxter's pharmacy products? Connect with us to learn more.
Please ask your Baxter representative how Baxter premixes can help your healthcare operations.

Wholesaler Services
The majority of Baxter's Pharmacy Products are available for order through your Wholesaler
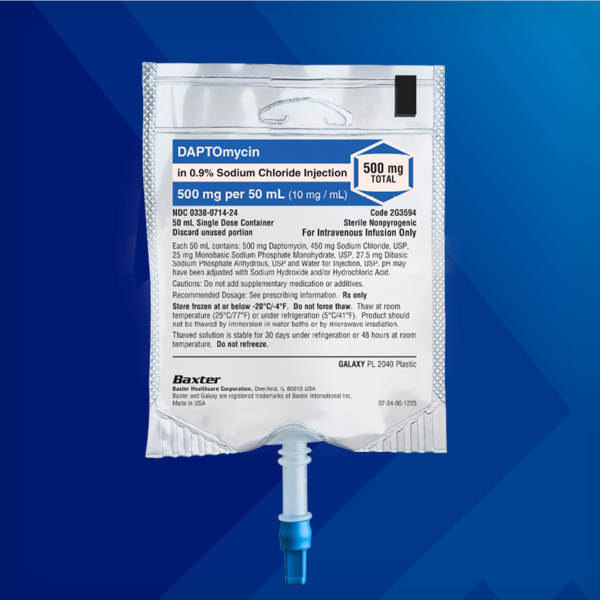
Daptomycin in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection
350 mg/50 mL, 500 mg/50 mL, 700 mg/100 mL, 1,000 mg/100 mL
Indications and Important Risk Information
Indications
Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection is a lipopeptide antibacterial indicated for the treatment of:
- Complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) in adult and pediatric patients (1 to 17 years of age) for whom appropriate dosing can be achieved and,
- Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections (bacteremia), in adult patients for whom appropriate dosing can be achieved, including those with right-sided infective endocarditis,
- Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections (bacteremia) in pediatric patients (1 to 17 years of age) for whom appropriate dosing can be achieved.
Limitations of Use:
- Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection is not indicated for the treatment of pneumonia.
- Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection is not indicated for the treatment of left-sided infective endocarditis due to S. aureus.
- Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection is not recommended in pediatric patients younger than one year of age due to the risk of potential effects on muscular, neuromuscular, and/or nervous systems (either peripheral and/or central) observed in neonatal dogs.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection should be used to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
Important Risk Information
Contraindications
- Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to daptomycin.
Warnings and Precautions
- Anaphylaxis/Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylaxis/hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with the use of antibacterial agents, including daptomycin for injection, and may be life-threatening. If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue the drug and institute appropriate therapy.
- Myopathy and Rhabdomyolysis: Patients receiving Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection should be monitored for the development of muscle pain or weakness, particularly of the distal extremities. CPK levels should be monitored weekly, and more frequently in patients who received recent, prior, or concomitant therapy with an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor or in whom elevations in CPK occur during treatment.
In adult patients with renal impairment, both renal function and CPK should be monitored more frequently than once weekly.
Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection should not be dosed more frequently than once a day.
Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection should be discontinued in patients with unexplained signs and symptoms of myopathy in conjunction with CPK elevations to levels >1,000 U/L, and in patients without reported symptoms who have marked elevations in CPK, with levels >2,000 U/L. - Eosinophilic Pneumonia: Has been reported in patients receiving daptomycin for injection. In reported cases, patients developed fever, dyspnea with hypoxic respiratory insufficiency, and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates or organizing pneumonia. In general, patients developed eosinophilic pneumonia 2 to 4 weeks after starting daptomycin for injection and improved when discontinued and steroid therapy was initiated. Recurrence of eosinophilic pneumonia upon re-exposure has been reported. Patients who develop these signs and symptoms should undergo prompt medical evaluation, and Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection should be discontinued immediately.
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): DRESS has been reported in post-marketing experience. Patients who develop skin rash, fever, peripheral eosinophilia, and systemic organ (for example, hepatic, renal, pulmonary) impairment while receiving Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection should undergo medical evaluation. If DRESS is suspected, discontinue promptly and institute appropriate treatment.
- Tubulointerstitial Nephritis (TIN): TIN has been reported in post-marketing experience. Patients who develop new or worsening renal impairment while receiving Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection should undergo medical evaluation. If TIN is suspected, discontinue promptly and institute appropriate treatment.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Cases have been reported during post-marketing experience. Therefore, physicians should be alert to signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection. Monitor for neuropathy and consider discontinuation.
- Potential Nervous System and/or Muscular System Effects in Pediatric Patients Younger than 12 Months: Avoid use in pediatric patients younger than 12 months due to the risk of potential effects on muscular, neuromuscular, and/or nervous systems (either peripheral and/or central) observed in neonatal dogs with intravenous daptomycin.
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD): CDAD has been reported with the use of nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including daptomycin for injection, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Careful medical history is necessary because CDAD has been reported to occur more than 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
- Persisting or Relapsing S. aureus Bacteremia/Endocarditis: Patients should have repeat blood cultures. If a blood culture is positive for S. aureus, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) susceptibility testing of the isolate should be performed, and diagnostic evaluation of the patient should be performed to rule out sequestered foci of infection. Appropriate surgical intervention and/or consideration of a change in antibacterial regimen may be required. Failure of treatment may be due to reduced daptomycin susceptibility.
- Decreased efficacy was observed in adult patients with moderate baseline renal impairment: Consider these data when selecting antibacterial therapy for use in adult patients with baseline moderate to severe renal impairment.
- Adverse Reactions:
- Adult cSSSI Patients: The most common adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of adult cSSSI patients receiving daptomycin for injection 4 mg/kg were diarrhea, headache, dizziness, rash, abnormal liver function tests, elevated creatine phosphokinase (CPK), urinary tract infections, hypotension, and dyspnea.
- Pediatric cSSSI Patients: The most common adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of pediatric patients receiving daptomycin for injection were diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, pruritus, pyrexia, elevated CPK, and headache.
- Adult S. aureus bacteremia/endocarditis Patients: The most common adverse reactions that occurred in ≥5% of S. aureus bacteremia/endocarditis patients receiving daptomycin for injection 6 mg/kg were sepsis, bacteremia, abdominal pain, chest pain, edema, pharyngolaryngeal pain, pruritus, increased sweating, insomnia, elevated CPK, and hypertension.
- Pediatric S. aureus bacteremia Patients: The most common adverse reactions that occurred in ≥5% of pediatric patients receiving daptomycin for injection were vomiting and elevated CPK.
- Drug Interactions:
- HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase may cause myopathy. Experience with the coadministration of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and daptomycin for injection in patients is limited; therefore, consideration should be given to suspending use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors temporarily in patients receiving Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection.
- Drug-Lab Test Interactions: Increased International Normalized Ratio (INR)/Prolonged Prothrombin Time: Clinically relevant plasma concentrations of daptomycin have been observed to cause a significant concentration-dependent false prolongation of prothrombin time (PT) and elevation of International Normalized Ratio (INR) when certain recombinant thromboplastin reagents are utilized for the assay.
Dosage and Administration
- If a dose of Daptomycin in Sodium Chloride Injection is required that does not equal 350 mg, 500 mg, 700 mg or 1,000 mg, this product is not recommended for use and an alternative formulation of daptomycin should be considered.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information for Daptomycin in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection.
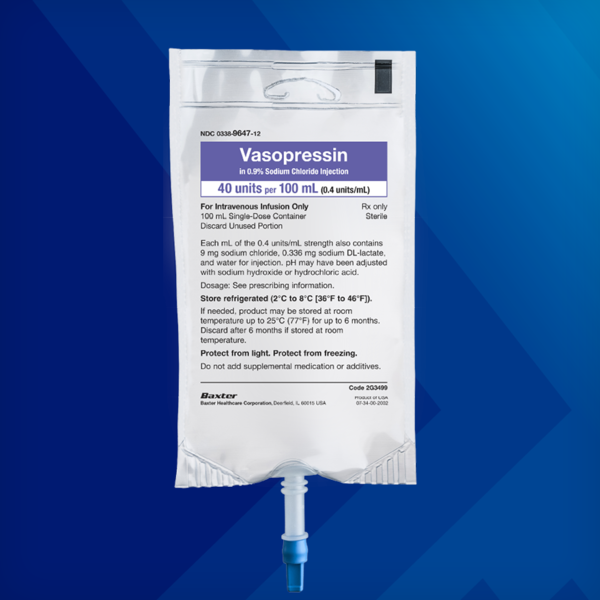
Vasopressin in 0.9% 100 mL Sodium Chloride Injection
20 units vasopressin (0.2 units/mL) in 0.9% 100 mL sodium chloride
40 units vasopressin (0.4 units/mL) in 0.9% 100 mL sodium chloride
Indications and Important Risk Information
Indications
- Vasopressin in Sodium Chloride Injection is indicated to increase blood pressure in adults with vasodilatory shock who remain hypotensive despite fluids and catecholamines.
Important Risk Information
- Contraindications: Vasopressin in Sodium Chloride Injection is contraindicated in patients with a known allergy or hypersensitivity to 8-L-arginine vasopressin.
- Worsening Cardiac Function: A decrease in cardiac index may be observed with the use of vasopressin.
- Reversible Diabetes Insipidus: Patients may experience reversible diabetes insipidus, manifested by the development of polyuria, a dilute urine, and hypernatremia, after cessation of treatment with vasopressin. Monitor serum electrolytes, fluid status, and urine output after vasopressin discontinuation. Some patients may require readministration of vasopressin or administration of desmopressin to correct fluid and electrolyte shifts.
- Adverse Reactions:
– The most common adverse reactions include decreased cardiac output, bradycardia, tachyarrhythmias, hyponatremia, and ischemia (coronary, mesenteric, skin, digital). - Drug Interactions:
– Pressor effects of catecholamines and Vasopressin in Sodium Chloride Injection are expected to be additive.
– Indomethacin may prolong effects of Vasopressin in Sodium Chloride Injection.
– Co-administration of ganglionic blockers or drugs causing SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion) may increase the pressor response.
– Co-administration of drugs causing diabetes insipidus may decrease the pressor response. - Pregnancy: May induce tonic uterine contractions that could threaten the continuation of pregnancy.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information for Vasopressin in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection.
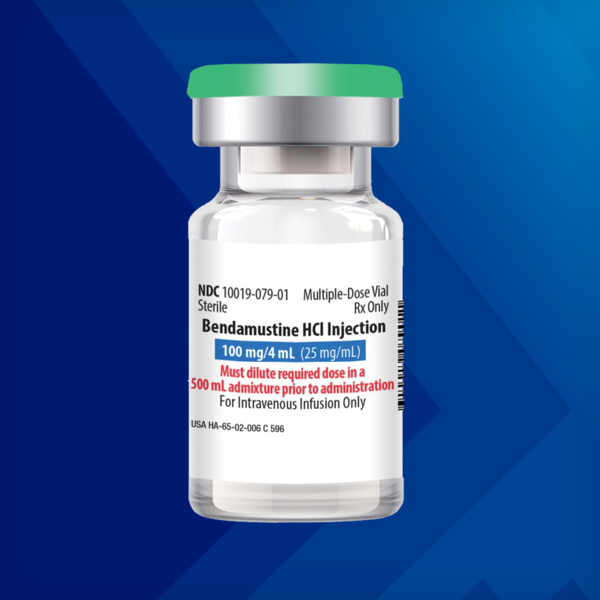
Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection
100 mg/4 mL (25 mg/mL) Multiple-Dose Vial
Indications and Important Risk Information
Indications
Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection is an alkylating drug indicated for treatment of adult patients with:
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Efficacy relative to first line therapies other than chlorambucil has not been established.
- Indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) that has progressed during or within six months of treatment with rituximab or a rituximab-containing regimen.
Important Risk Information
Contraindications
Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions) to bendamustine, polyethylene glycol 400, alcohol, or monothioglycerol.
Warnings and Precautions
-
Myelosuppression: Bendamustine hydrochloride caused severe myelosuppression (Grade 3-4) in 98% of patients in the two NHL studies. Three patients (2%) died from myelosuppression-related adverse reactions. Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection causes myelosuppression. Monitor complete blood counts, including leukocytes, platelets, hemoglobin (Hgb), and neutrophils frequently. Hematologic nadirs were observed predominantly in the third week of therapy. Myelosuppression may require dose delays and/or subsequent dose reductions if recovery to the recommended values has not occurred by the first day of the next scheduled cycle. Prior to the initiation of the next cycle of therapy, the ANC should be ≥ 1 x 109 /L and the platelet count should be ≥ 75 x 109 /L.
-
Infections: Infection, including pneumonia, sepsis, septic shock, hepatitis and death has occurred in adult and pediatric patients in clinical trials and in postmarketing reports for bendamustine hydrochloride. Patients with myelosuppression following treatment are more susceptible to infections; advise patients to contact a physician immediately if they have symptoms or signs of infection. Patients are at risk for reactivation of infections including (but not limited to) hepatitis B, cytomegalovirus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and herpes zoster. Patients should undergo appropriate measures for infection and infection reactivation prior to administration.
-
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML): PML, including fatal cases, have occurred following treatment with bendamustine, primarily in combination with rituximab or obinutuzumab. Consider PML in the differential diagnosis in patients with new or worsening neurological, cognitive or behavioral signs or symptoms. If PML is suspected, withhold Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection treatment and perform appropriate diagnostic evaluations. Consider discontinuation or reduction of any concomitant chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy in patients who develop PML.
-
Anaphylaxis and Infusion Reactions: Infusion reactions to bendamustine hydrochloride have occurred commonly in clinical trials. Symptoms include fever, chills, pruritus and rash. In rare instances severe anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have occurred, particularly in the second and subsequent cycles of therapy. Patients who experience Grade 3 or worse allergic-type reactions should not be rechallenged. Consider measures to prevent severe reactions in subsequent cycles in patients who have experienced Grade 1 or 2 infusion reactions. Discontinue Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection for patients with Grade 4 infusion reactions. Consider discontinuation for Grade 3 infusion reactions as clinically appropriate.
-
Tumor Lysis Syndrome: Tumor lysis syndrome associated with bendamustine hydrochloride has occurred in patients in clinical trials and in post-marketing reports. The onset tends to be within the first treatment cycle and, without intervention, may lead to acute renal failure and death. Preventive measures include vigorous hydration and close monitoring of blood chemistry, particularly potassium and uric acid levels. Allopurinol has also been used during the beginning of bendamustine hydrochloride therapy. However, there may be an increased risk of severe skin toxicity when bendamustine hydrochloride and allopurinol are administered concomitantly.
-
Skin Reactions: Fatal and serious skin reactions have been reported with bendamustine hydrochloride treatment in clinical trials and postmarketing safety reports, including toxic skin reactions [Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), bullous exanthema, and rash]. Events occurred when bendamustine hydrochloride was given as a single agent and in combination with other anticancer agents or allopurinol. Where skin reactions occur, they may be progressive and increase in severity with further treatment. Monitor patients with skin reactions closely. If skin reactions are severe or progressive, withhold or discontinue Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection.
-
Hepatotoxicity: Fatal and serious cases of liver injury have been reported with Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection. Combination therapy, progressive disease or reactivation of hepatitis B were confounding factors in some patients. Most cases were reported within the first three months of starting therapy. Monitor liver chemistry tests prior to and during therapy.
-
Other Malignancies: There are reports of pre-malignant and malignant diseases that have developed in patients who have been treated with bendamustine hydrochloride. Monitor patients for the development of secondary malignancies. Perform dermatologic evaluations during and after treatment.
-
Extravasation Injury: Bendamustine hydrochloride extravasations have been reported in postmarketing resulting in hospitalizations from erythema, marked swelling, and pain. Assure good venous access prior to starting and monitor the intravenous infusion site for redness, swelling, pain, infection, and necrosis during and after administration.
-
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Based on findings from animal reproduction studies and the drug’s mechanism of action, Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use an effective method of contraception during treatment and for 6 months after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose.
-
Adverse Reactions:
-
Adverse reactions (frequency >5%) during infusion and within 24 hours post-infusion are nausea and fatigue.
-
Most common adverse reactions (≥15%) for CLL are anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, leukopenia, hyperbilirubinemia, pyrexia, nausea, vomiting.
-
Most common adverse reactions (≥15%) for NHL are lymphopenia, leukopenia, anemia neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea, pyrexia, constipation, anorexia, cough, headache, weight decreased, dyspnea, rash, and stomatitis.
-
-
Drug Interactions:
-
CYP1A2 Inhibitors: The coadministration with CYP1A2 inhibitors may increase bendamustine plasma concentrations and may result in increased incidence of adverse reactions with Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection. Consider alternative therapies that are not CYP1A2 inhibitors during treatment.
-
CYP1A2 Inducers: The coadministration with CYP1A2 inducers may decrease bendamustine plasma concentrations and may result in decreased efficacy of Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection. Consider alternative therapies that are not CYP1A2 inducers during treatment.
-
-
Use in Specific Populations:
-
Infertility: Based on findings from clinical studies and animal studies, Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection may impair male fertility.
-
Renal Impairment: Do not use Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection in patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) < 30 mL/min.
-
Hepatic Impairment: Do not use Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection in patients with AST or ALT 2.5-10 × upper limit of normal (ULN) and total bilirubin 1.5-3 × ULN, or total bilirubin > 3 × ULN.
-
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information for Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection.