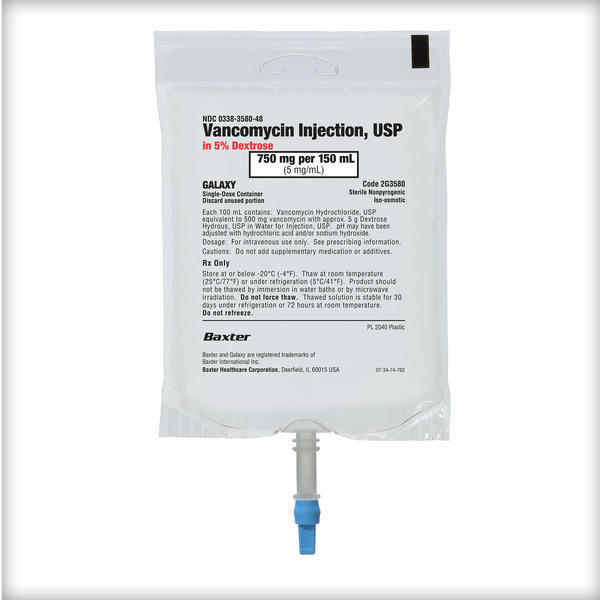
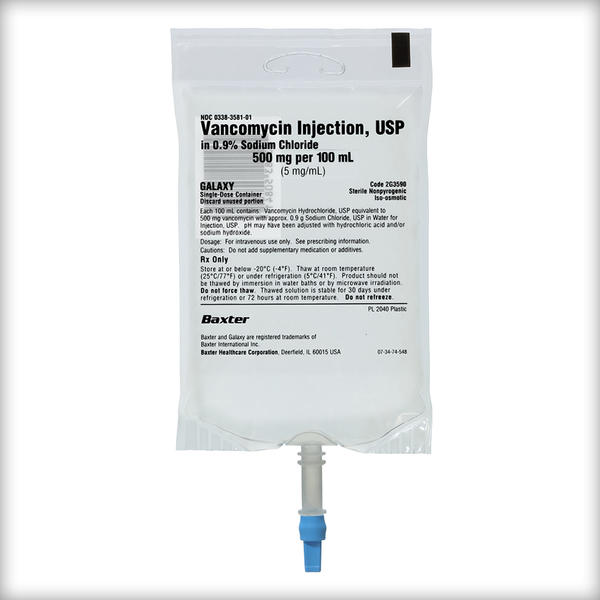
Frozen Premix Vancomycin Injection, USP
Select Indications and Important Risk Information
Vancomycin Injection, USP
Vancomycin Injection is a glycopeptide antibacterial indicated for the treatment of the following infections in adult and pediatric patients for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved: Septicemia, Infective Endocarditis, Skin and Skin Structure Infections, Bone Infections, Lower Respiratory Tract Infections.
Contraindications: Vancomycin Injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to vancomycin. Solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with known allergy to corn or corn products.
Please read the accompanying full Indications and Important Risk Information and full Prescribing Information

Vancomycin Injection, USP
When it comes to high-volume medications like IV vancomycin, we know that more options in a premix formulation mean you can treat more patients with the safety of a premix, with more efficiency and less waste.1-3
That’s why Baxter has added 2 strengths to expand its offering of Vancomycin Injection in Dextrose to a total of 5 doses, to help you support patient care.
Vancomycin Injection, USP in 0.9% Sodium Chloride
By Phone
Government Customer Service
Baxter is the leader in frozen premix IV anti-infectives.4 Premix Vancomycin for patient safety considerations and operational efficiency.
Safety
- Standardized concentration may help reduce medication errors associated with compounding preparation1,2
- Barcoded for bedside scanning to help ensure the right patient gets the right medication2
Efficiency
- No admixing or batching required—which may help streamline deployment and save pharmacy time and resources
- Premix medications like Vancomycin support inventory management and help reduce waste3
Consistent concentration
A manufacturer-prepared vancomycin injection helps ensure that patients receive a consistent concentration of medication2
Add Vancomycin to your Premix portfolio
Reach out to your Baxter sales representative. Don’t have one? Call: 1.888.229.0001
Or visit: Product eCatalog
Baxter offers practical and innovative products in premix ready-to-use IV formulations, including frozen, which may increase hospital efficiency while helping to support patient care.
How might your institution benefit from adding additional Baxter premixes?
- SAFETY: Reducing the potential for medication errors due to compounding1,2
- EFFICIENCY: Improved workflow by allowing on-demand availability of medications
- VALUE: Manufacturer-prepared premix medications have a shelf life of 9 to 24 months
- PATIENT CARE: Potentially shortening the time between ordering and administration may allow you to spend more time with your patients
Vancomycin Injection, USP
Indications and Important Risk Information
Indications
Vancomycin Injection is a glycopeptide antibacterial indicated for the treatment of the following infections in adult and pediatric patients for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved:
- Septicemia
- Infective Endocarditis
- Skin and Skin Structure Infections
- Bone Infections
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Vancomycin Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Vancomycin Injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria.
Important Risk Information
- Contraindications: Vancomycin Injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to vancomycin. Solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with known allergy to corn or corn products.
- Infusion Reactions: Hypotension, including shock and cardiac arrest, wheezing, dyspnea, urticaria or pruritus, muscular and chest pain may occur with rapid Vancomycin Injection administration. The reactions may be more severe in pediatric patients. Rapid intravenous administration may also be associated with “vancomycin infusion reaction”, which manifests as pruritus and erythema that involves the face, neck and upper body. There have been reports that the frequency of infusion-related reactions increases with the concomitant administration of anesthetic agents. Infusion-related adverse reactions are related to both the concentration and rate of administration.
Administer Vancomycin Injection over a period of 60 minutes or greater prior to administration of anesthetic agents when feasible. Stopping the infusion usually results in prompt cessation of these reactions. - Nephrotoxicity: Vancomycin Injection can result in acute kidney injury (AKI), including acute renal failure. The risk of AKI increases with higher vancomycin serum levels, prolonged exposure, concomitant administration of other nephrotoxic drugs, concomitant administration of piperacillin-tazobactam, volume depletion, pre-existing renal impairment and in critically ill patients and patients with co-morbid conditions that predispose to renal impairment. Monitor serum vancomycin concentrations and renal function in all patients. If AKI occurs, discontinue Vancomycin Injection, or reduce the dose.
- Ototoxicity: Has occurred in patients receiving Vancomycin Injection. It may be reversible or permanent. Ototoxicity manifests as tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness or vertigo. The risk is higher in older patients, patients who are receiving higher doses, who have an underlying hearing loss, who are receiving concomitant therapy with another ototoxic agent, or who have underlying renal impairment. Monitor serum vancomycin concentrations and renal function in all patients. Discontinue Vancomycin Injection if ototoxicity occurs. Serial tests of auditory function may be helpful in order to minimize the risk.
- Severe Dermatologic Reactions: Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD) have been reported. Cutaneous signs or symptoms reported include skin rashes, mucosal lesions, and blisters. Discontinue Vancomycin Injection at the first appearance of signs and symptoms of TEN, SJS, DRESS, AGEP, or LABD.
- Clostridioides difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD): CDAD has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Vancomycin Injection, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
- Hemorrhagic Occlusive Retinal Vasculitis (HORV): HORV, including permanent loss of vision, occurred in patients receiving intracameral or intravitreal administration of vancomycin during or after cataract surgery. The safety and efficacy of vancomycin administered by the intracameral or the intravitreal route have not been established.
- Neutropenia: Reversible neutropenia has been reported. Patients who will undergo prolonged therapy with vancomycin or those who are receiving concomitant drugs that may cause neutropenia should have periodic monitoring of the leukocyte count. Neutropenia appears to be promptly reversible when vancomycin is discontinued.
- Phlebitis and Other Administration Site Reactions: Inflammation at the injection site has been reported. Vancomycin is irritating to tissue and must be given by a secure intravenous route of administration. Thrombophlebitis may occur, the frequency and severity of which can be minimized by slow infusion of the drug and by rotation of venous access sites.
- Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions are anaphylaxis, “vancomycin infusion reaction”, acute kidney injury, hearing loss, neutropenia.
- Drug Interactions:
- Anesthetic Agents: Concomitant administration of vancomycin and anesthetic agents has been associated with erythema and histamine-like flushing.
- Piperacillin/Tazobactam: Increased incidence of acute kidney injury in patients receiving concomitant piperacillin/tazobactam as compared to vancomycin alone. Monitor kidney function in patients.
- Renal Impairment: Dosage adjustment of Vancomycin Injection must be made in patients with impaired renal function. Measure vancomycin serum concentrations to guide intravenous therapy, especially in patients with impaired renal function or fluctuating renal function.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information for Vancomycin Injection, USP.